What is the principle of corrosion resistance of titanium metal materials?
- Share
- publisher
- andy
- Issue Time
- Sep 26,2021
Summary
Titanium is a very corrosion-resistant metal. However, the thermodynamic data of titanium metal materials show that titanium is a thermodynamically unstable metal. If iron can dissolve to Ti2+, the standard electrode has a negative potential (-1,63V) and is always covered with a dull titanium oxide film.In this way, the stable potential of iron is stably positive. For example, the stable potential of titanium in seawater at 25℃ is about +0.09V.
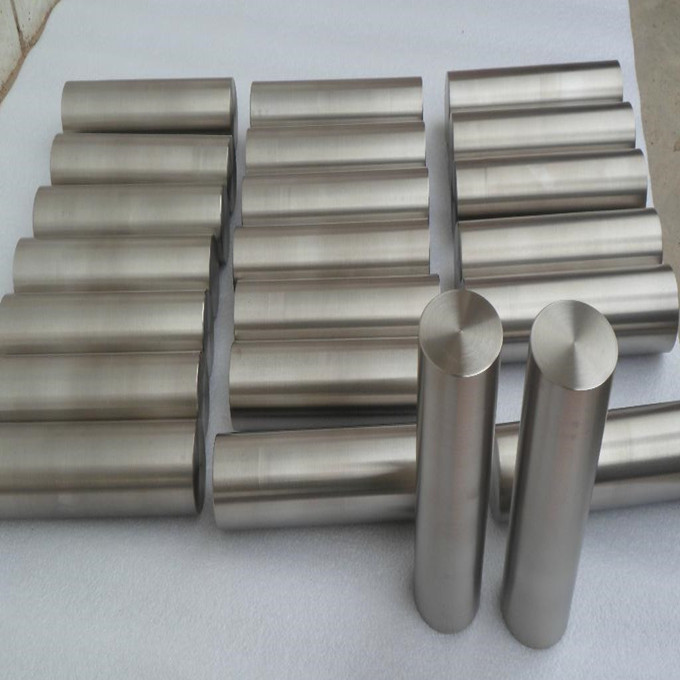

Titanium metal materials the most common is titanium sheet,titanium bar,titanium wire,titanium pipe.
Titanium is a very corrosion-resistant metal. However, the thermodynamic data of titanium show that titanium is a thermodynamically unstable metal. If iron can dissolve to Ti2+, the standard electrode has a negative potential (-1,63V) and is always covered with a dull titanium oxide film.In this way, the stable potential of iron is stably positive. For example, the stable potential of titanium in seawater at 25℃ is about +0.09V.
Potential data of titanium electrode reactionshows that its surface is very active, usually covered with a layer of oxide film, which is naturally generated in the air. It is this layer of stable, strong adhesion, strong protective oxide film, which determines the excellent corrosion resistance of titanium. Theoretically, the Pilling/Bedworth ratio of the protective oxide film must be greater than 1. If less than 1, the oxide film cannot completely cover the metal surface and has no protective .
When the surface of titanium is exposed to the atmosphere or aqueous solution, a new oxide film will be generated immediately. For example, the thickness of the oxide film in the atmosphere at room temperature is about 1.2~1.6nm, and thickens with time. After 70 days, it naturally thickens to 5nm, and after 545 days, it gradually increases to 8~9 nm. Artificial enhancement of oxidation conditions (such as heating, oxidizing or anodic oxidation, etc.) can accelerate the growth of oxide film on the surface and obtain a thicker oxide film, thus improving the corrosion resistance of titanium. Therefore, anodic oxidation and thermal oxidation of the oxide film, will significantly improve the titanium oxide film (including thermal oxidation film or anodic oxidation film) is usually not a single titanium corrosion resistance.
The composition and structure of the oxide vary with the formation conditions. In general, the interface between oxide film and environment may be TiO2, while the interface between oxide film and metal may be dominated by TiO. There may be transition layers with different valence states in the middle, or even non-chemical equivalent oxides, which indicates that titanium oxide film has multilayer structure. As for the formation process of this oxide film, it can not be simply understood as the result of direct reaction between titanium and oxygen.